Tatics that enhanced and accelerated raytracing
Anti-Aliasing
Aliasing is when the change between pixels is too sudden to be realistic to the image, creating a unrealistic image. In raytracing this can happen when not enough rays are sampled for a pixel.

Super Sampling
Aliasing occurs when the sampling (i.e. shooting rays) is down too far apart, leading to certain areas of a pixel which could have a different value not being sampled
Adaptive Sampling
The basic idea of adaptive sampling is to add more sample points (rays) in areas that show indications of inbetween values not being sampled
Distribution Raycasting
Instead of adding more rays to get the correct sample, we can use a distribution (specifically the poisson distribution) to determine the best place on the pixel to sample our ray
Acceleration
Ray-Polyhedron Intersection
There are many ways to handle intersection with triangle based objects
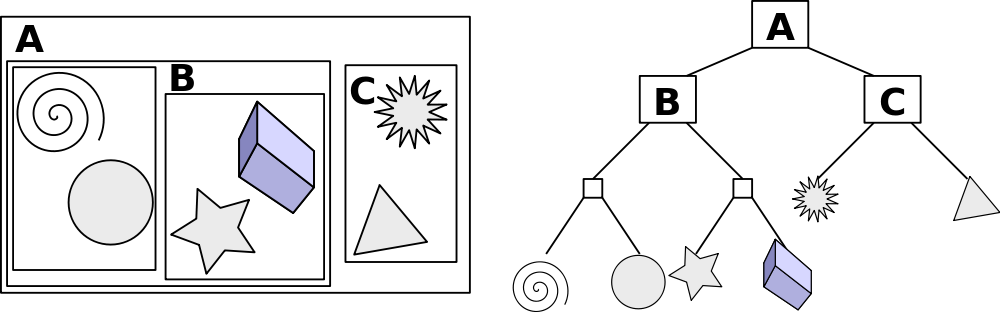
Bounding Volume
You can using a bounding volume to determine if you are touching an object. This allows you to use primitives to determine intersection while costing accuracy
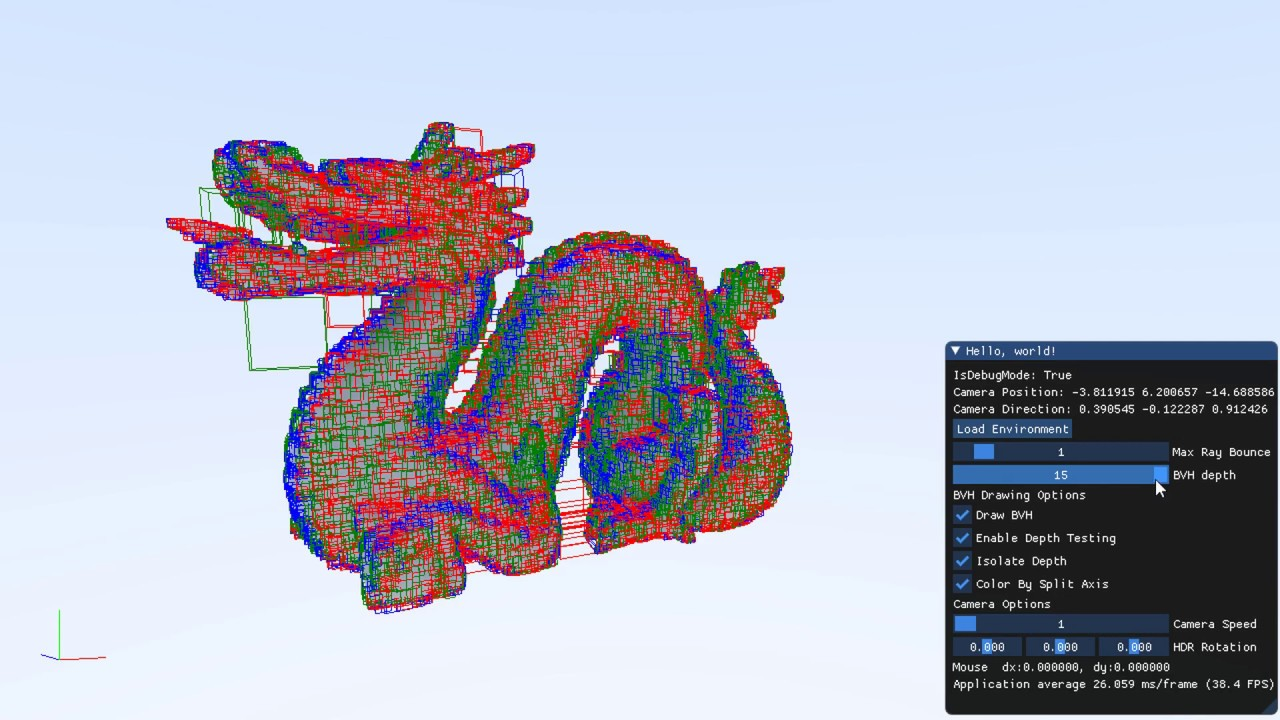
Bounding Voluming Hierarchy
Instead of only giving the overall object a bounding volume, you can do a hierarichal tree of boudning volumes that also seperate pieces of the objects in volumes
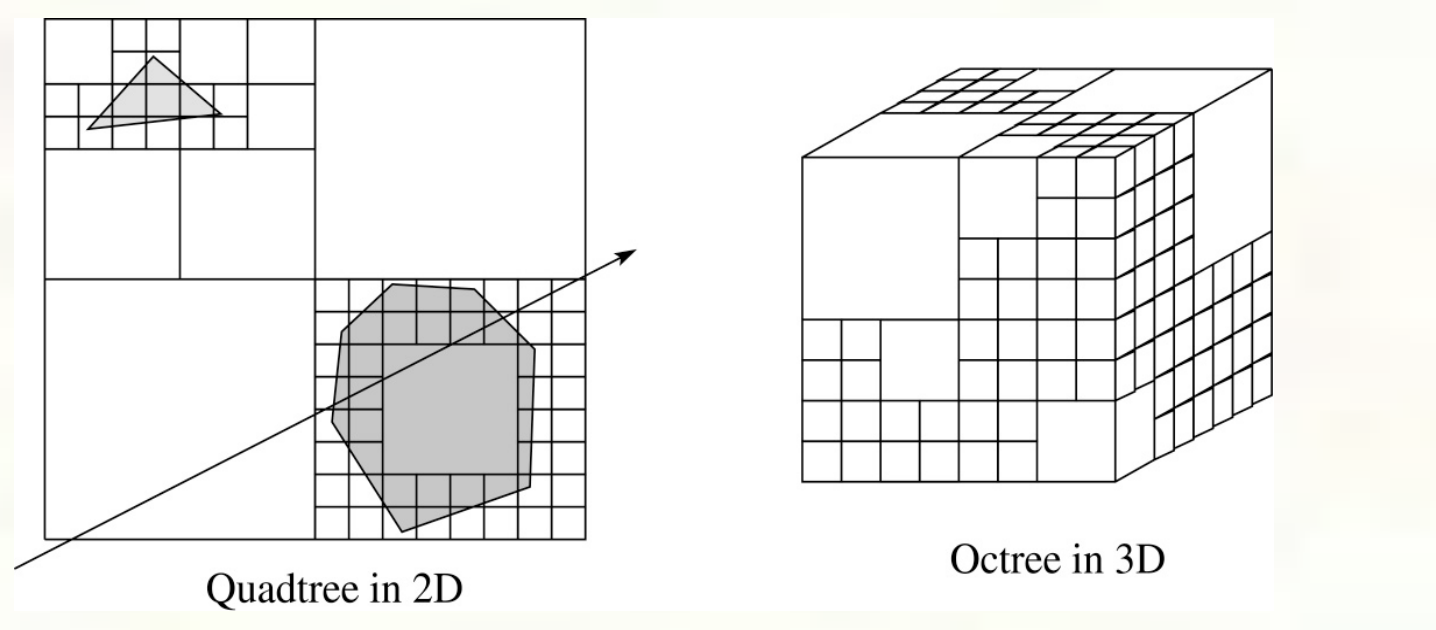
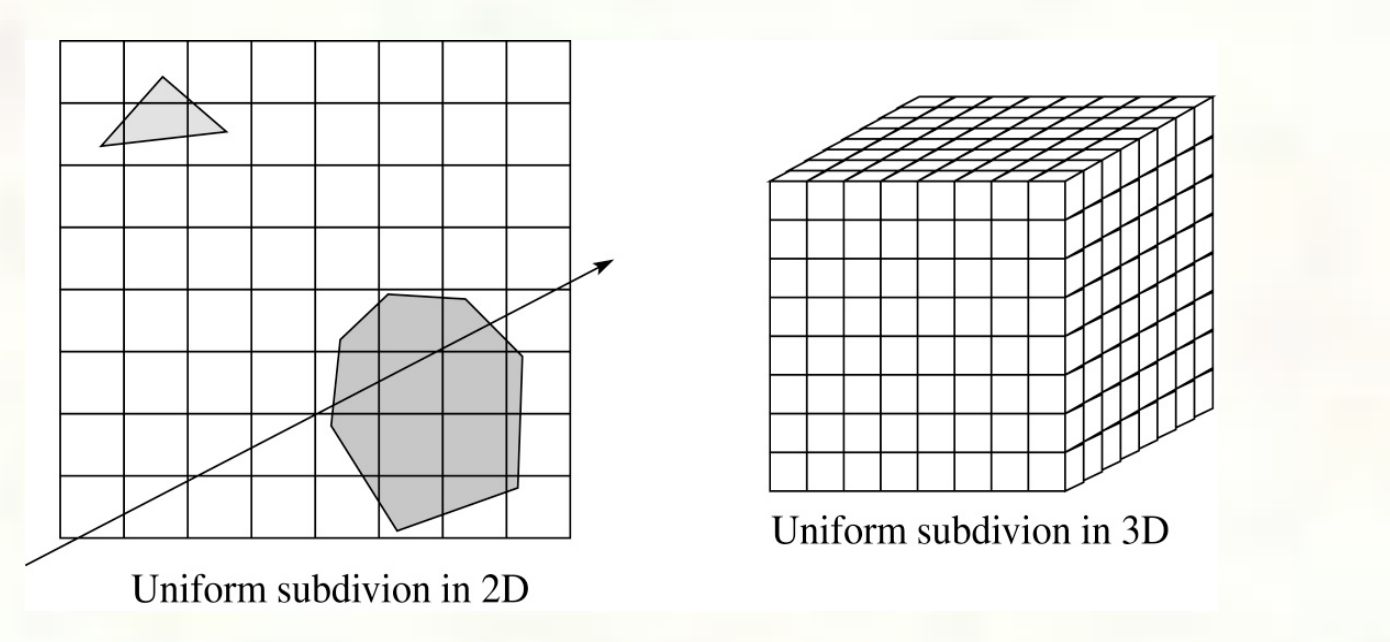
Spatial Subdivision
Uniform
The idea of spatial subdivision is to divide the world space into cells uniformally and tying objects to the cells it overlaps
Non-Uniform
As the name suggests, it’s the same idea of the uniform method but with the cells being non-uniformally subdivided